Who is Lev Vigotsky?
Vigotsky is one of the great educational theorists of the 20th century. His contributions have had an impact on our current models of education, and his theories have given rise to multiple conceptions applied to modern-day pedagogy.
Vigotsky’s socio-cultural theory seeks to lay the foundations of how learning is built up gradually during the early years, and with the help of the social context of the youngest children.
What is Vigotsky’s sociocultural theory?
Vygotsky’s theory shows how learning is built up gradually during the early years and with the help of the child’s social context. Lev Vigotsky argued that children gradually develop their learning through social interaction: they acquire new and improved skills, as well as the logical process of their immersion into a familiar, routine way of life.
Likewise, this sociocultural theory of cognitive development focuses not only on how adults and peers, through collaborative work, influence individual learning, but also on how cultural beliefs and attitudes impact the way instruction and learning take place.
According to Vygotsky, children still have a long period of brain development ahead of them. In addition, each culture provides what he called tools of intellectual adaptation. These tools allow children to use their basic mental abilities in ways that are sensitive to the culture in which they grow up.

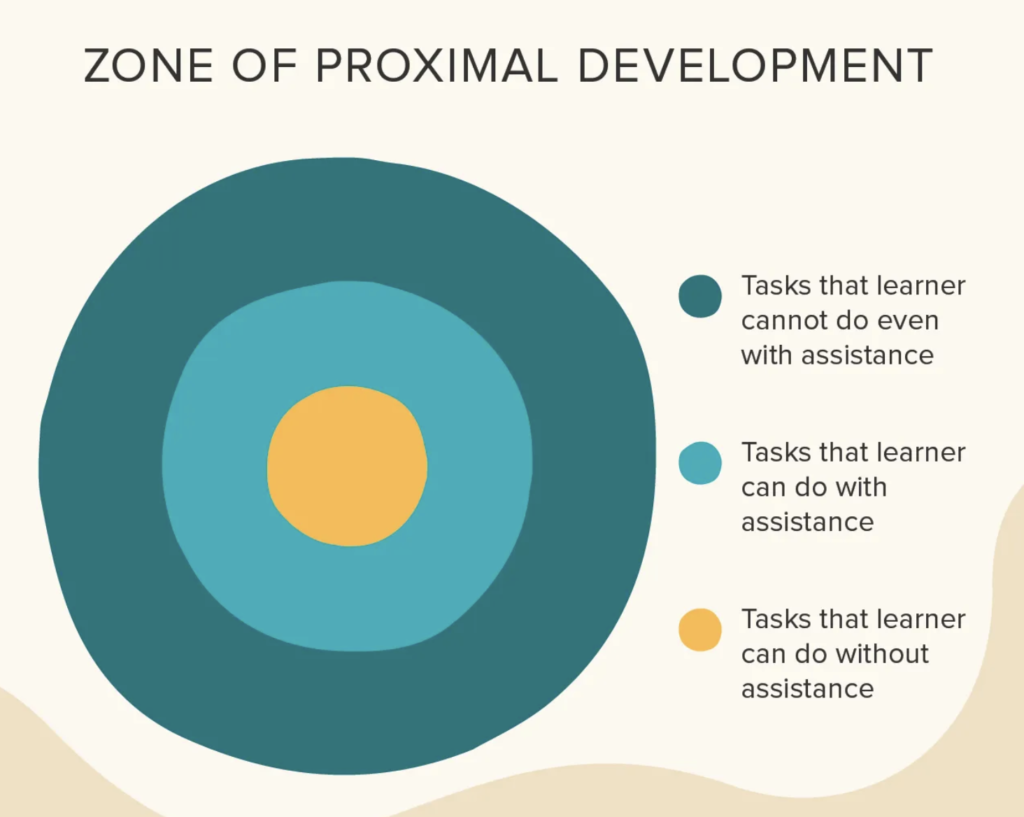
What is the Zone of Proximal Development (ZDP)?
Vigotsky created three zones of development: the zone of actual development, which represents the current abilities of the pupil, the zone of proximal development where the pupil is in the process of formation and the zone of potential development, which would be the level that the child can reach with the help of a person.
The zone of proximal development refers to the space that exists between the current psychic development of the subject, i.e. the skills that the child already possesses and his or her potential development (what he or she can learn through guidance). For this reason it is a concept of utmost importance for education at all levels of education.
That is to say, according to Vygotsky, the role of adults or more advanced peers is to support, direct and organise the child’s learning, in the step prior to the child being able to master these facets, having internalised the behavioural and cognitive structures that the activity demands.
This orientation is most effective in helping young children to cross the zone of proximal development (ZDP), which could be understood as the gap between what they are already able to do and what they cannot yet achieve on their own.
How can we apply it in class?
Vygotsky believed that children learn more efficiently in a social environment. That is why learning to use social development theory in a classroom can help your students understand ideas more quickly.
Furthermore, social interaction for Lev plays an integral role in learning and promotes a reciprocal teaching style. It is for this reason that today we would like to give you some advice on how to apply this theory in the classroom.
Our main advice is to let the students be the protagonists of their own learning: Design activities in which you are not in front of the class all the time, i.e. ask more questions than you answer.
- establish activities and games that stimulate the pupils’ zone of proximal development.
- structure the activities according to levels of difficulty during the learning process
- bet for a collaborative rather than an individual work
- implement playful activities that facilitate social interaction.